Now Service Host: Local System is itself a bundle of other system processes which run under it, in other words, it’s basically a generic service hosting container. So troubleshooting this issue becomes a lot difficult as any process under it can cause the high CPU usage problem. Service Host: Local System includes a process such as a User Manager, Group Policy Client, Windows Auto Update, Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS), Task Scheduler etc. In general, Service Host: Local System can take a lot of CPU & RAM resources as it has a number of different processes running under it but if a particular process is constantly taking a large chunk of your system resources then it can be a problem. So without wasting any time let’s see how to Fix High CPU Usage by Service Host: Local System with the help of below-listed troubleshooting guide.
Fix High CPU Usage by Service Host: Local System
Make sure to create a restore point just in case something goes wrong.
Fix High CPU Usage by Service Host: Local System Method 1: Disable Superfetch Method 2: Run SFC and DISM Method 3: Registry Fix Method 4: Run Windows Update troubleshooter Method 5: Perform a Clean boot Method 6: Restart Windows Update service Method 7: Change Processor Scheduling Method 8: Disable Background Intelligent Transfer Service Method 9: Disable Certain Services
Method 1: Disable Superfetch
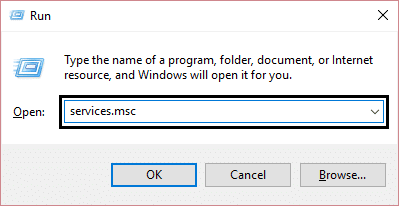
1.Press Windows Key + R then type services.msc and hit Enter.
2.Find Superfetch service from the list then right-click on it and select Properties.
3.Under Service status, if the service is running click on Stop. 4.Now from the Startup type drop-down select Disabled.
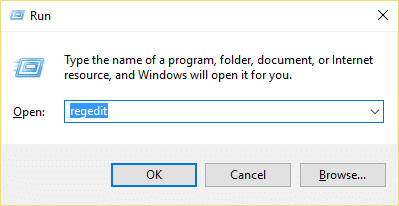
5.Click Apply followed by OK. 6.Reboot your PC to save changes. If the above method doesn’t disable Superfetch services then you can follow disable Superfetch using Registry: 1.Press Windows Key + R then type regedit and hit Enter to open Registry Editor.
2.Navigate to the following registry key: 3.Make sure you have selected PrefetchParameters then in the right window double click on EnableSuperfetch key and change it’s value to 0 in the value data field.
4.Click OK and close the Registry Editor. 5.Restart your PC to save changes and see if you’re able to Fix High CPU Usage by Service Host: Local System.
Method 2: Run SFC and DISM
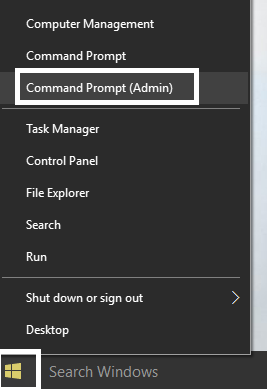
1.Press Windows Key + X then click on Command Prompt(Admin).
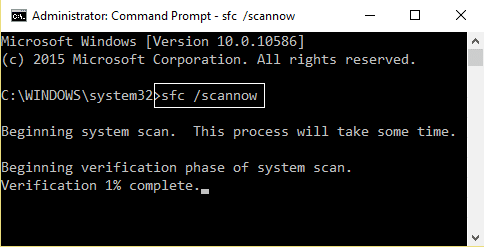
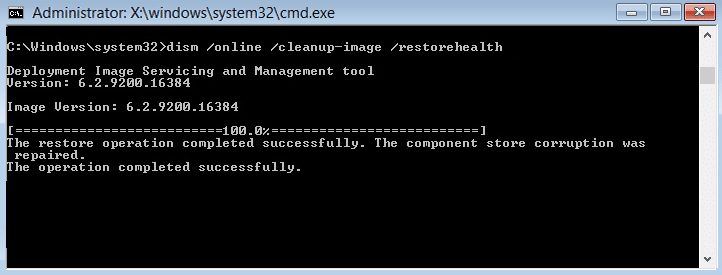
2.Now type the following in the cmd and hit enter:
3.Wait for the above process to finish and once done restart your PC. 4.Again open cmd and type the following command and hit enter after each one:
5.Let the DISM command run and wait for it to finish. 6. If the above command doesn’t work then try on the below: Note: Replace the C:\RepairSource\Windows with the location of your repair source (Windows Installation or Recovery Disc). 7.Reboot your PC to save changes and see if you’re able to Fix High CPU Usage by Service Host: Local System.
Method 3: Registry Fix
1.Press Windows Key + R then type regedit and hit Enter to open Registry Editor.
2.Navigate to the following registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\Ndu 3.Make sure to select Ndu then in the right window pane double-click on Start.
4.Change the value of Start to 4 and click OK.
5.Close everything and reboot your PC to save changes.
Method 4: Run Windows Update troubleshooter
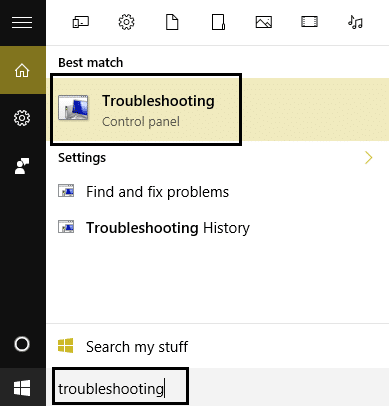
1.Now type “troubleshooting” in Windows Search bar and click on Troubleshooting.
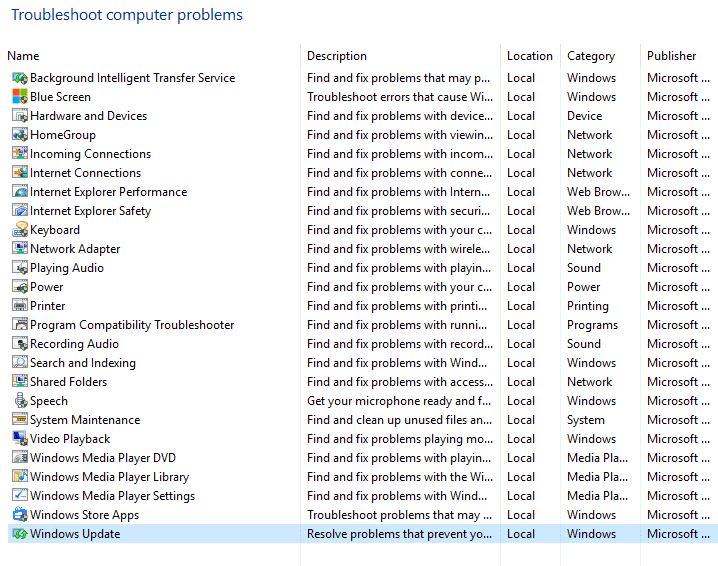
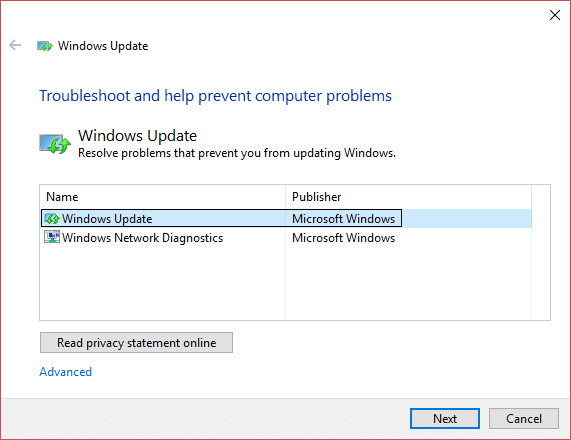
2.Next, from the left window pane select View all. 3.Then from the Troubleshoot computer problems list select Windows Update.
4.Follow on-screen instruction and let the Windows Update Troubleshoot run.
5.Restart your PC and you may be able to Fix High CPU Usage by Service Host: Local System.
Method 5: Perform a Clean boot
Sometimes 3rd party software can conflict with System and therefore can cause high CPU usage on your PC. In order to Fix High CPU Usage by Service Host: Local System, you need to perform a clean boot on your PC and diagnose the issue step by step.
Method 6: Restart Windows Update service
1.Press Windows Key + R then type “services.msc” (without quotes) and hit Enter.
2.Locate the following services: Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) Cryptographic Service Windows Update MSI Installer 3.Right-click on each of them and then select Properties. Make sure their Startup type is set to Automatic.
4.Now if any of the above services are stopped, make sure to click on Start under Service Status. 5.Next, right-click on Windows Update service and select Restart.
6.Click Apply followed by OK and then reboot your PC to save changes.
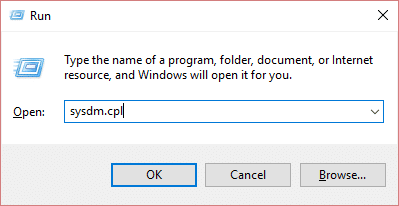
Method 7: Change Processor Scheduling
1.Press Windows Key + R then type sysdm.cpl and hit Enter to open System Properties.
2.Switch to the Advanced tab and click on Settings under Performance.
3.Again switch to Advanced tab under Performance Options. 4.Under Processor scheduling select Program and click Apply followed by OK.
5.Reboot your PC to save changes.
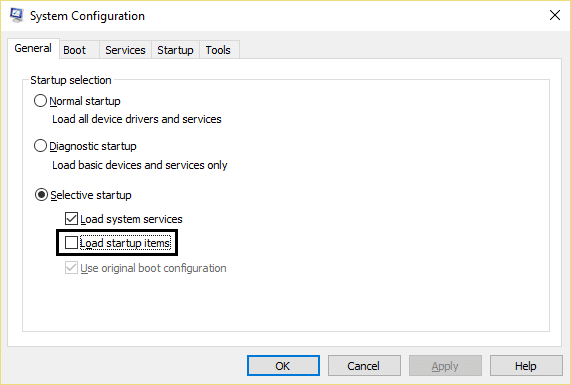
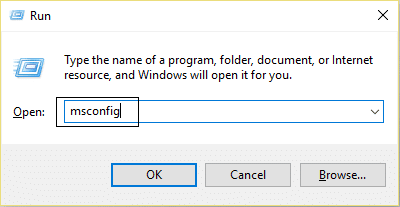
Method 8: Disable Background Intelligent Transfer Service
1.Press Windows Key + R then type msconfig and hit Enter.
2.Switch to services tab then uncheck “Background Intelligent Transfer Service”.
3.Click Apply followed by OK.
Method 9: Disable Certain Services
1.Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
2.Expand Service Host: Local System and see which service is taking up your system resources (high). 3.Select that service then right-click on it and select End Task.
4.Reboot your PC to save changes and if you still find that particular service taking high CPU usage then disable it. 5.Right-click on the service which you earlier shortlisted and select Open Services.
6.Find the particular service then right-click on it and select Stop. 7.Reboot your PC to save changes. Recommended:
Fix One or more network protocols are missing on this computer Fix You’ve been signed in with a temporary profile error How to Fix Desktop Refers to A Location That Is Unavailable Fix WiFi doesn’t connect automatically in Windows 10
That’s it you have successfully Fix High CPU Usage by Service Host: Local System but if you still have any questions regarding this post then feel free to ask them in the comment’s section.